Respiro
Continuous Respiratory Rate Monitoring During Motion via Wearable Ultra-Wideband Radar
IEEE-EMBS BHI 2024Abstract
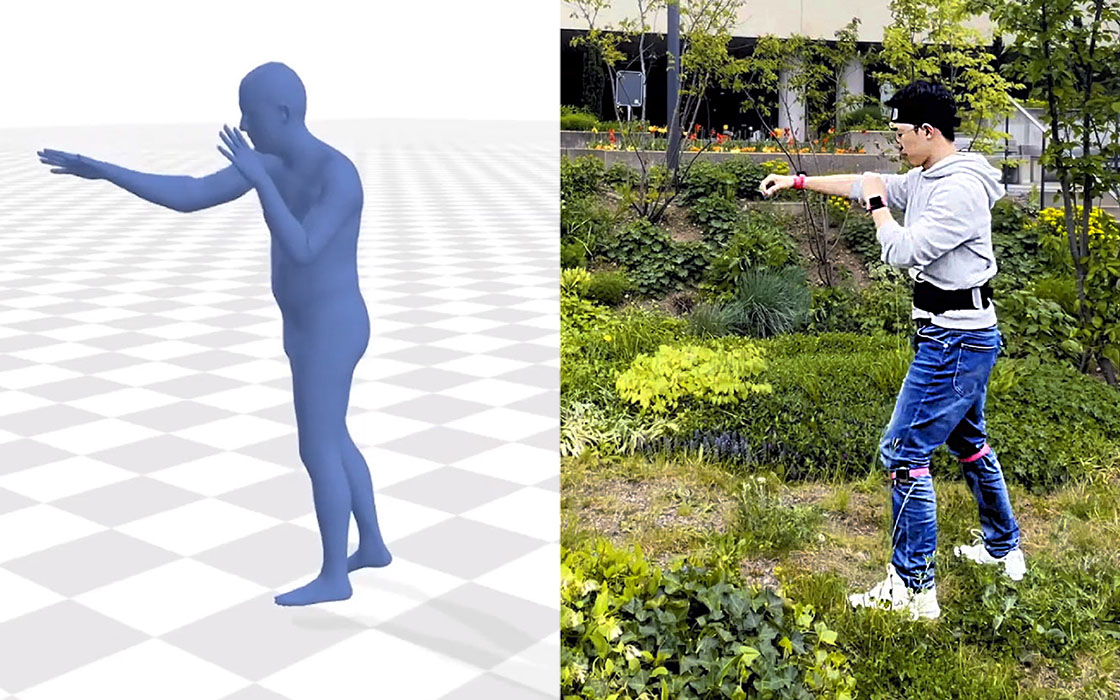
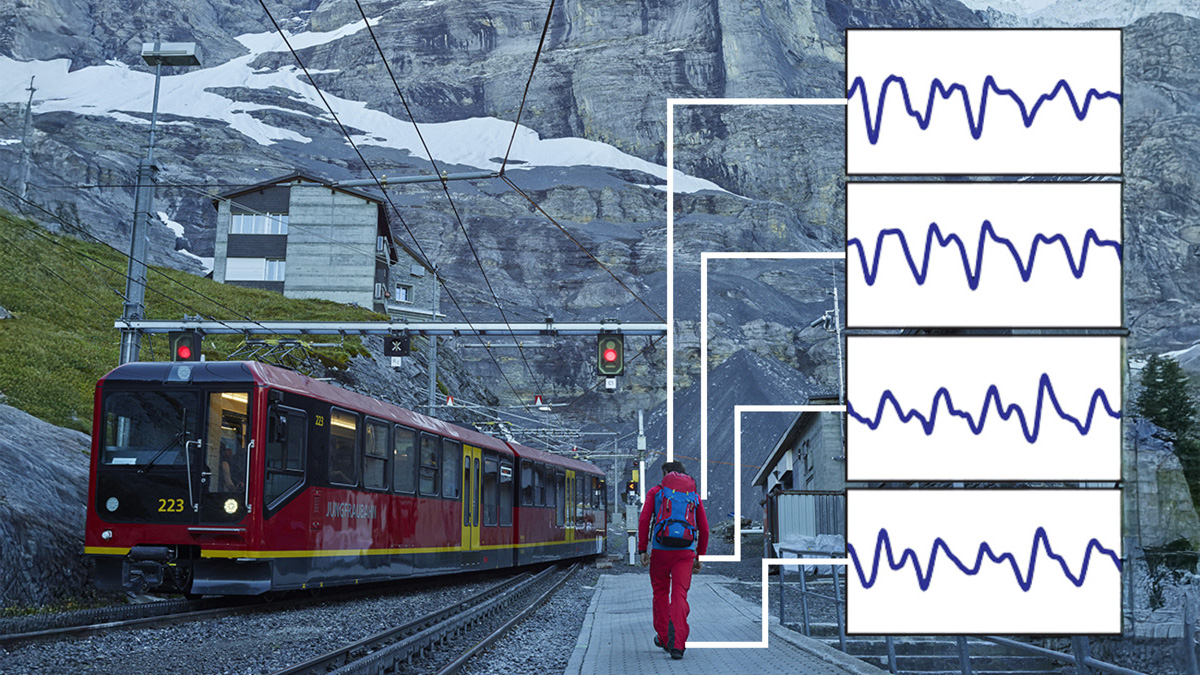
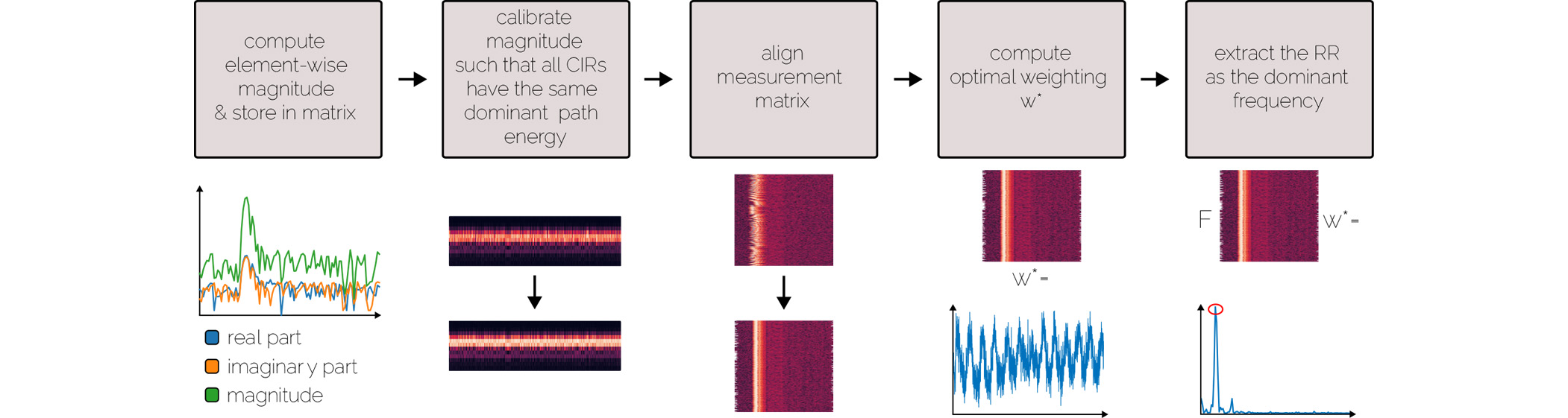
Deviations in respiratory rate often precede abnormalities in other vital signs. However, continuously monitoring respiratory rates outside clinical settings remains challenging due to the obtrusive nature and sensitivity to body motions in existing monitoring approaches. In this study, we propose a single-point-of-contact wearable device that leverages off-the-shelf, consumergrade ultra-wideband radar to monitor respiratory rate as part of a chest strap. Our signal processing pipeline reliably extracts the wearer’s respiratory signal from windowed complex channel impulse responses. In a controlled experiment, twelve participants performed various activities to evaluate the system’s accuracy under motion while capturing ground-truth recordings through a spirometer. Our method extracted respiratory rates with less than 1 breath per minute deviation in 71% of all measurements, averaging 1.11 breaths per minute across all sessions and participants. Our findings underscore the potential of consumer-grade ultra-wideband radar technology in bodyworn devices for unobtrusive yet effective respiratory monitoring.
Reference
Sebastian Reidy, Manuel Meier, and Christian Holz. Respiro: Continuous Respiratory Rate Monitoring During Motion via Wearable Ultra-Wideband Radar. In International Conference on Biomedical and Health Informatics 2024 (IEEE-EMBS BHI).