Accurately Tracking Relative Positions on Moving Trackers based on UWB Ranging and Inertial Sensing without Anchors
IEEE IROS 2024Abstract
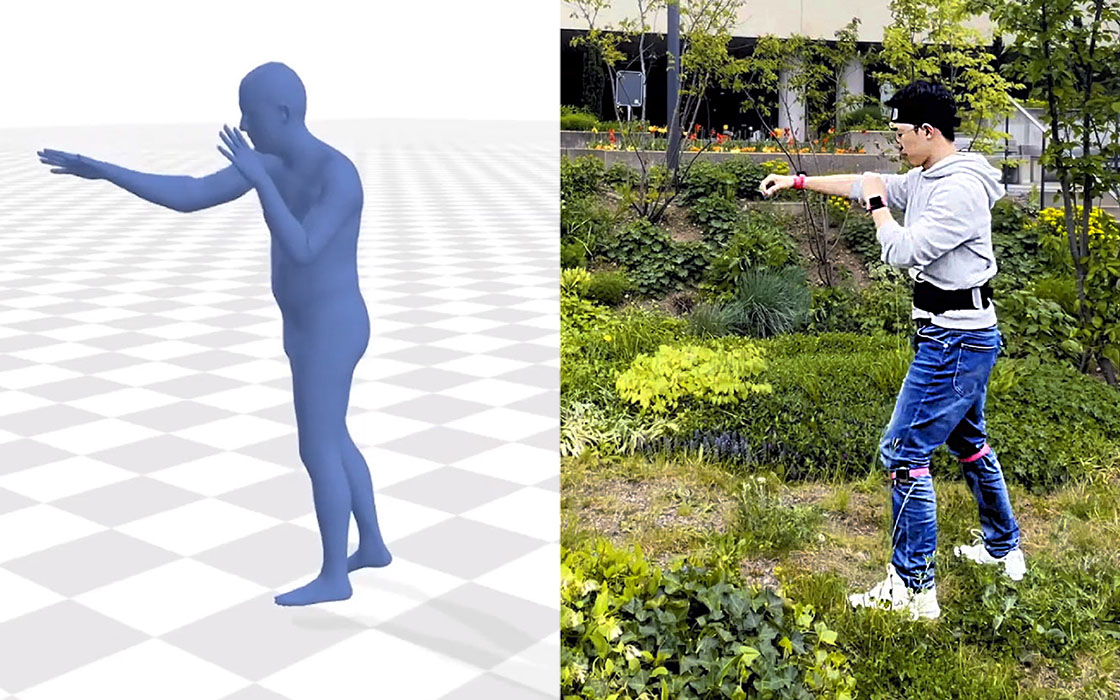
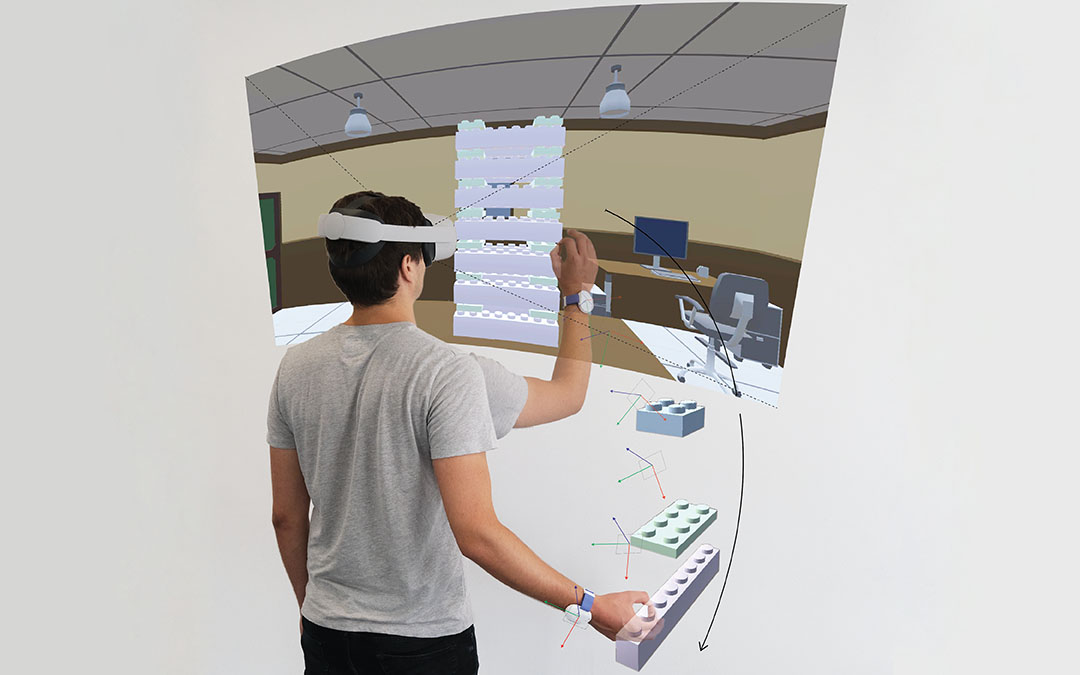
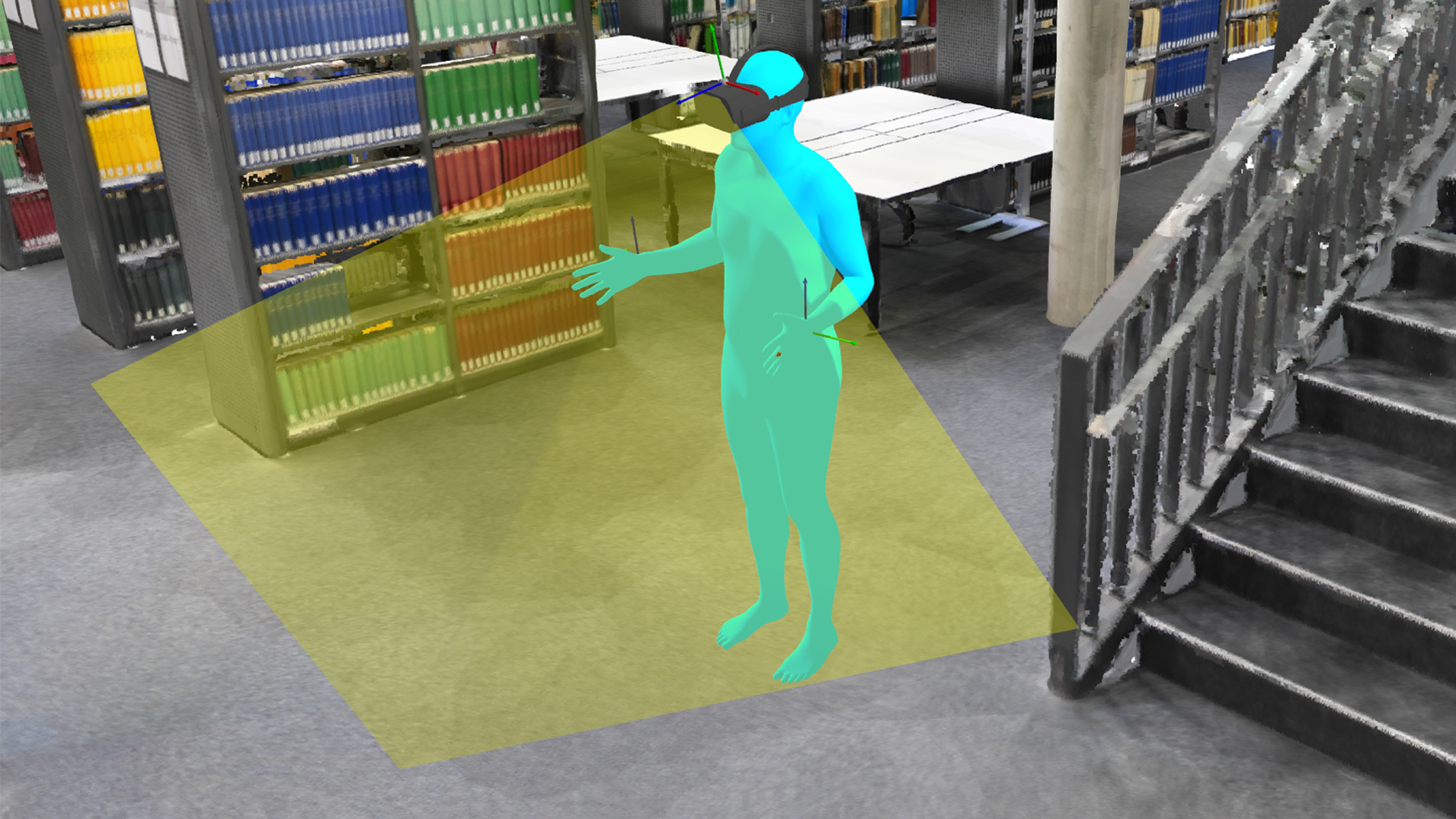
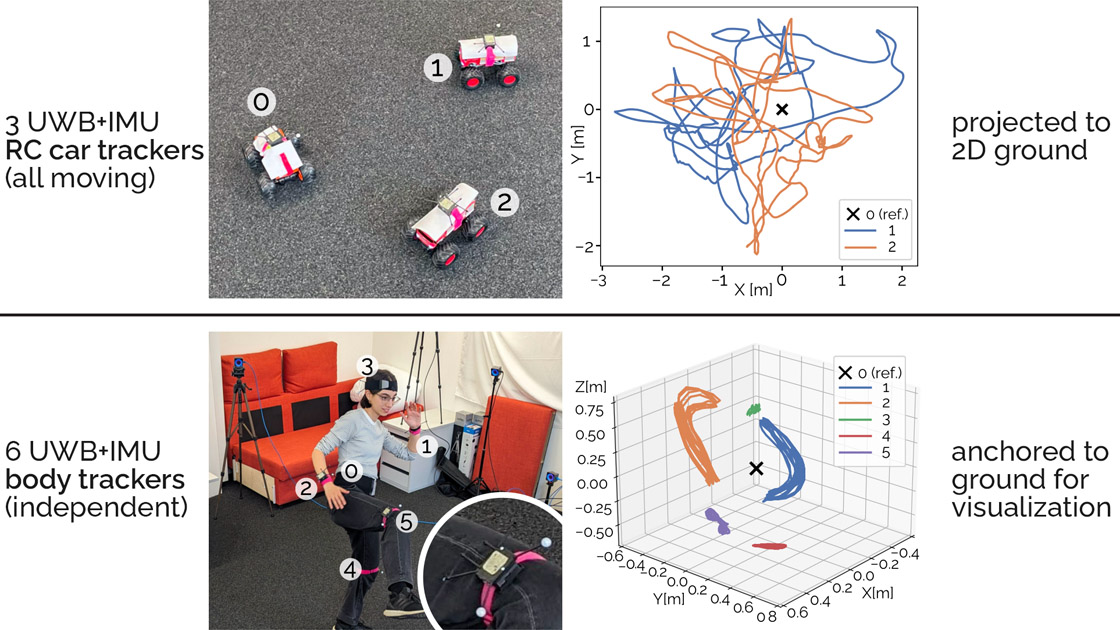
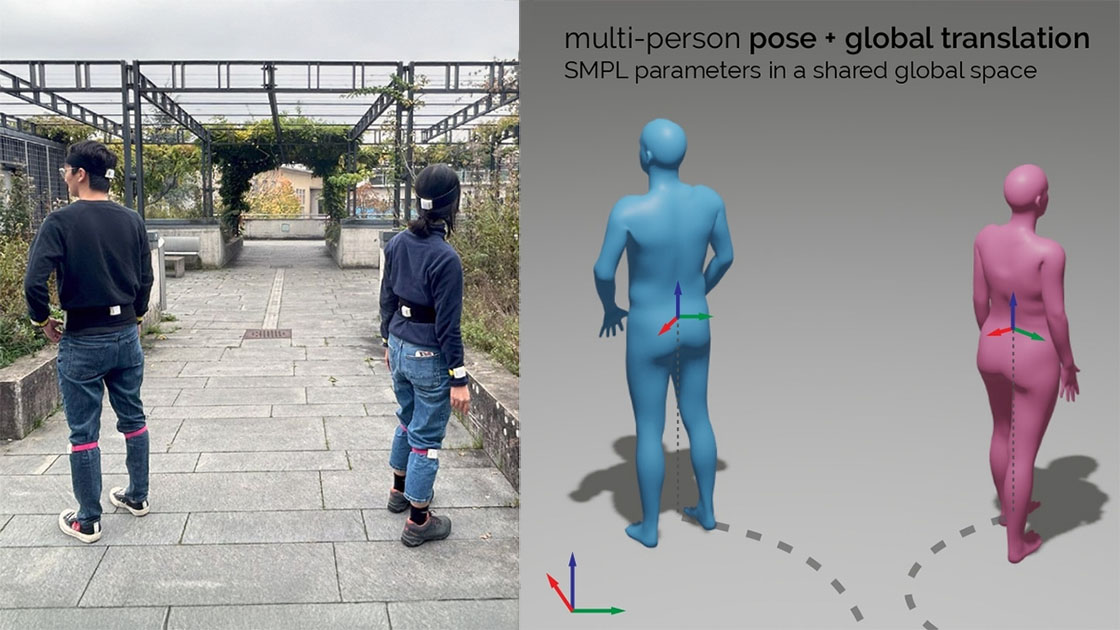
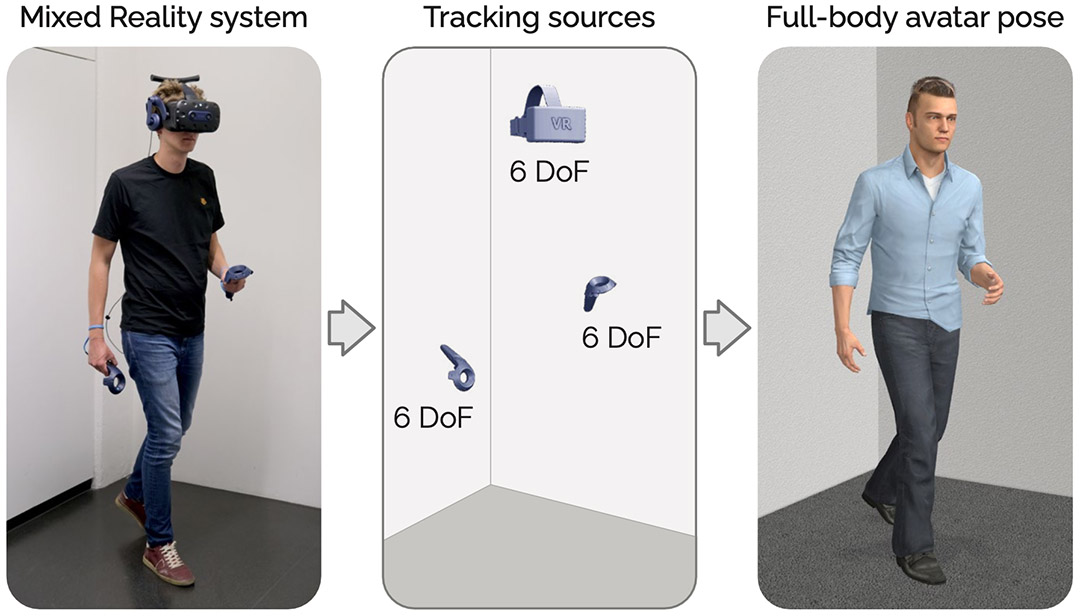
We present a tracking system for relative positioning that can operate on entirely moving tracking nodes without the need for stationary anchors. Each node embeds a 9-DOF magnetic and inertial measurement unit and a single-antenna ultra-wideband radio. We introduce a multi-stage filtering pipeline through which our system estimates the relative layout of all tracking nodes within the group. The key novelty of our method is the integration of a custom Extended Kalman filter (EKF) with a refinement step via multidimensional scaling (MDS). Our method integrates the MDS output back into the EKF, thereby creating a dynamic feedback loop for more robust estimates. We complement our method with UWB ranging protocol that we designed to allow tracking nodes to opportunistically join and leave the group.
In our evaluation with constantly moving nodes, our system estimated relative positions with an error of 10.2 cm (in 2D) and 21.7 cm (in 3D), including obstacles that occluded the line of sight between tracking nodes. Our approach requires no external infrastructure, making it particularly suitable for operation in environments where stationary setups are impractical.
Reference
Rayan Armani and Christian Holz. Accurately Tracking Relative Positions on Moving Trackers based on UWB Ranging and Inertial Sensing without Anchors. In International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems 2024 (IEEE IROS).