egoEMOTION
Egocentric Vision and Physiological Signals for Emotion and Personality Recognition in Real-World Tasks
NeurIPS 2025Abstract
Understanding affect is central to anticipating human behavior, yet current egocentric vision benchmarks largely ignore the person’s emotional states that shape their decisions and actions. Existing tasks in egocentric perception focus on physical activities, hand-object interactions, and attention modeling—assuming neutral affect and uniform personality. This limits the ability of vision systems to capture key internal drivers of behavior. In this paper, we present egoEMOTION, the first dataset that couples egocentric visual and physiological signals with dense self-reports of emotion and personality across controlled and real-world scenarios. Our dataset includes over 50 hours of recordings from 43 participants, captured using Meta’s Project Aria glasses. Each session provides synchronized eye-tracking video, headmounted photoplethysmography, inertial motion data, and physiological baselines for reference. Participants completed emotion-elicitation tasks and naturalistic activities while self-reporting their affective state using the Circumplex Model and Mikels’ Wheel as well as their personality via the Big Five model. We define three benchmark tasks: (1) continuous affect classification (valence, arousal, dominance); (2) discrete emotion classification; and (3) trait-level personality inference. We show that a classical learning-based method, as a simple baseline in real-world affect prediction, produces better estimates from signals captured on egocentric vision systems than processing physiological signals. Our dataset establishes emotion and personality as core dimensions in egocentric perception and opens new directions in affect-driven modeling of behavior, intent, and interaction.
Video
Reference
Matthias Jammot*, Bjoern Braun*, Paul Streli, Rafael Wampfler, and Christian Holz. egoEMOTION: Egocentric Vision and Physiological Signals for Emotion and Personality Recognition in Real-World Tasks. In Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2025 (Datasets and Benchmarks, NeurIPS).
Data Collection
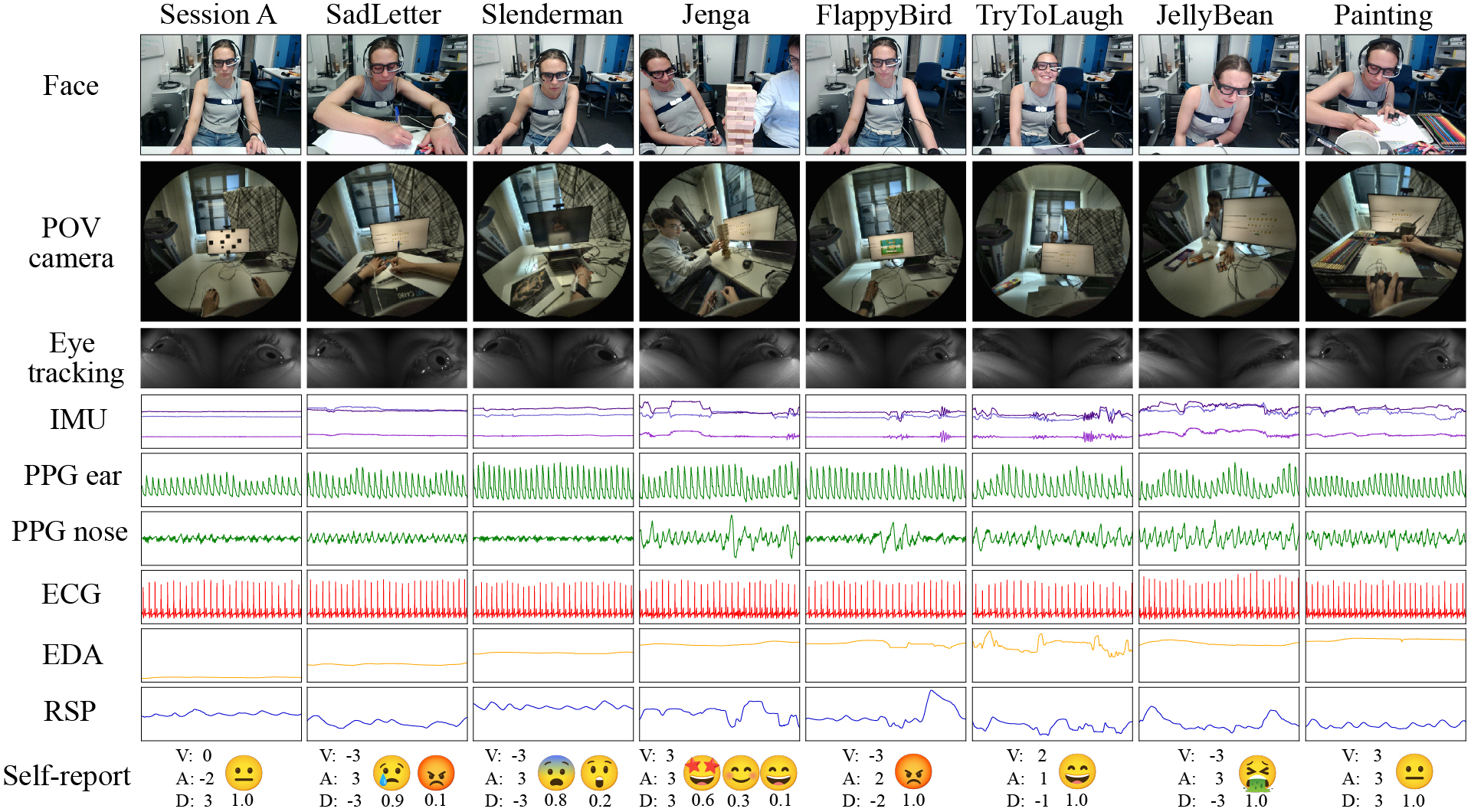
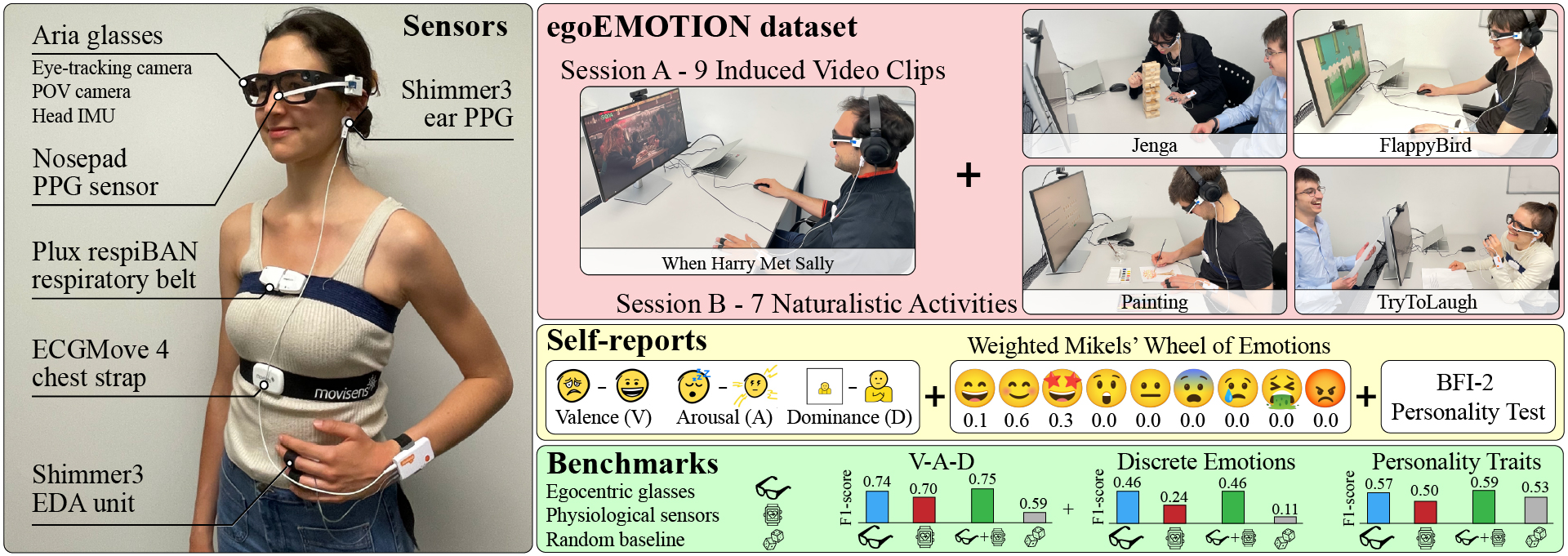
Figure 2. Visualization of all recorded sensors from the egocentric glasses and physiological sensors during each task with their associated self-reports.
Study Protocol
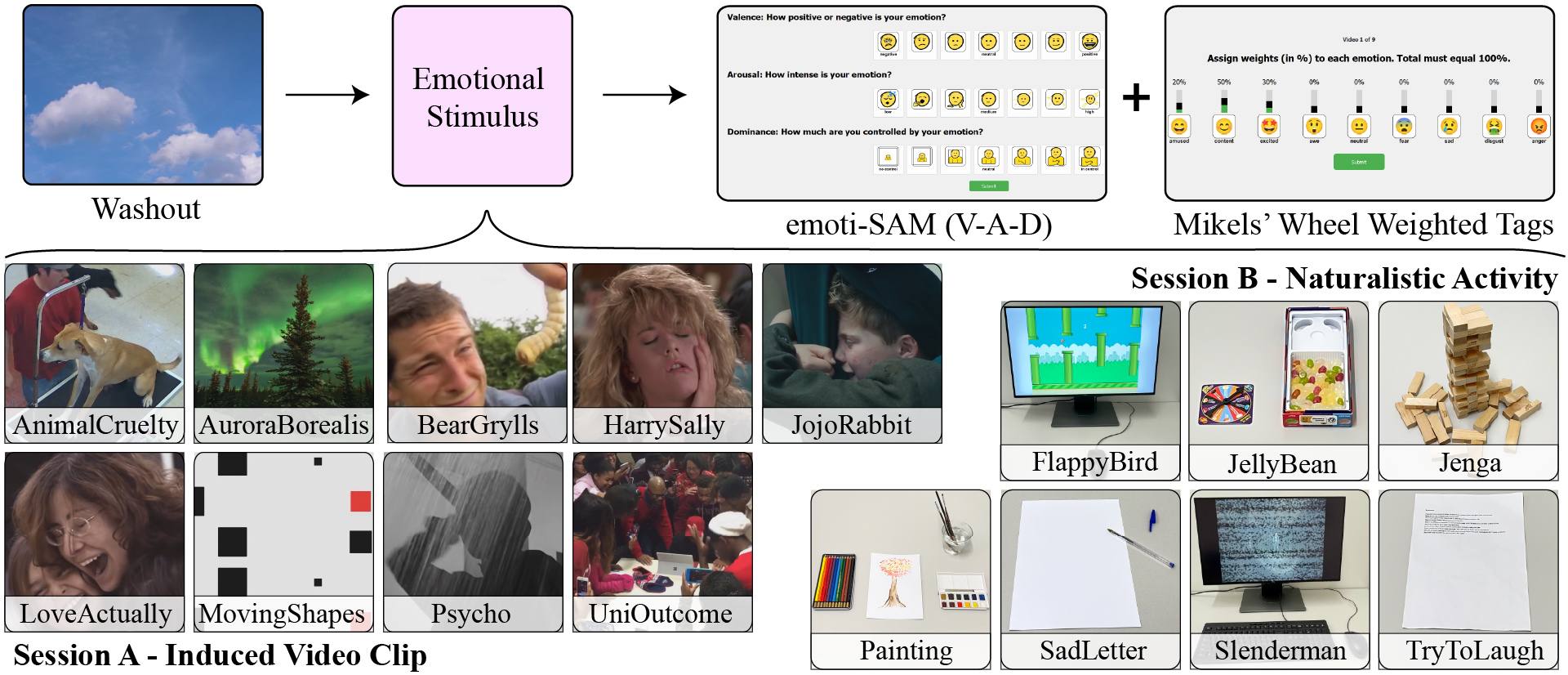
Figure 3. Overview of the experimental protocol. The experiment consisted of two sessions. In session A, participants watched 9 video clips, with a 40 s washout between clips and a 5 s video of a cross preceding each clip. In session B, participants performed 7 real-world tasks. Each task was spaced by a 1-min washout clip. Two questionnaires, corresponding to the emoti-SAM and a weighted Mikels’ Wheel were answered after each emotional stimulus.
Self-Reports
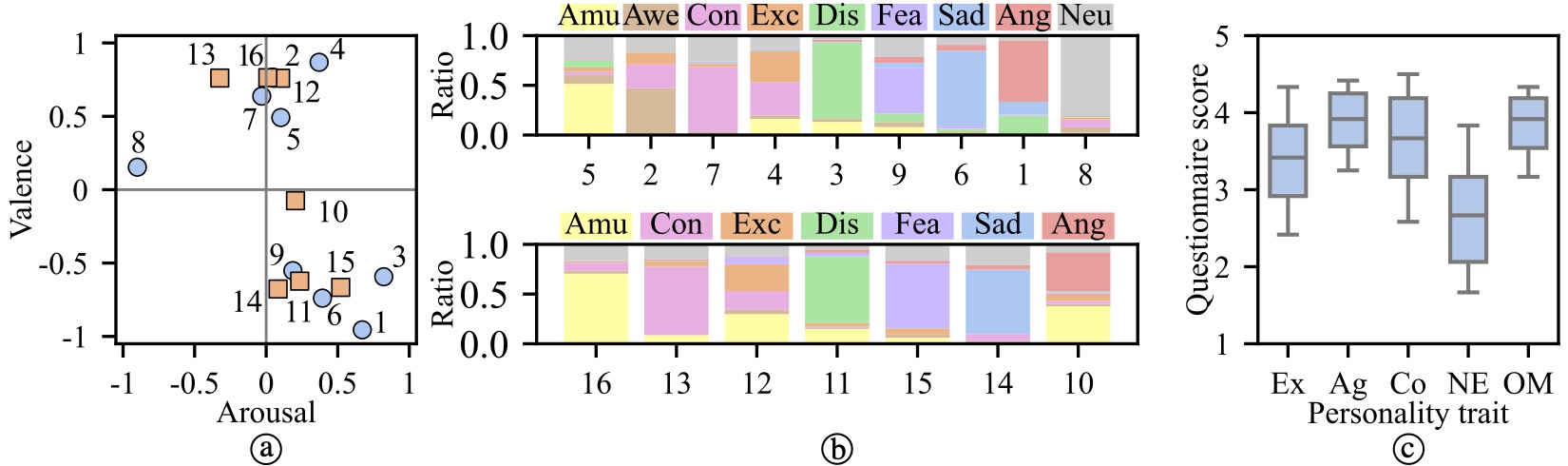
Figure 4. Participant self-reports across tasks. (a) Mean arousal-valence ratings. (b) Proportions of discrete emotions reported in Sessions A and B. (c) Boxplots of Big Five personality trait scores.